Development
This document explains you how to get started with developing harbor-sync. It shows you how to install the prerequisites and how to build, test and run the controller.
Get the code
$ git clone https://github.com/moolen/harbor-sync.git ~/dev/harbor-sync
$ cd ~/dev/harbor-syncInstalling the test environment
Prerequisites:
- Vagrant must be installed
- Minikube must be installed
- Kubebuilder must be installed
Use the provided Vagrantfile to spin up a harbor instance.
$ vagrant upRight now you need to click your way through harbor to create the projects for testing.
Once the installation is done harbor tells you the ip address for this installation (e.g. http://172.28.128.XXX.xip.io.).
If it is not yet running ssh into the machine and try to start the containers with docker-compose:
$ vagrant ssh
vagrant@harbor:~$ sudo docker-compose -f harbor/docker-compose.yml up -dTell the manager to access this deployment using environment variables:
$ export HARBOR_API_ENDPOINT=http://172.28.128.XXX.xip.io.
$ export HARBOR_USERNAME="admin"
$ export HARBOR_PASSWORD="Harbor12345"Next, deploy the CRD and run the controller:
$ make generate # gen crds & manifests
$ make install # install crds
$ make run
Developing
Now you’re set to do your changes. Please keep in mind:
if you add a feature, please add documentation about the usage and write tests that cover at least the happy path
run
make e2eto run e2e tests
Commit Messages
This projects follows the Conventional Commits specification.
Documentation
The documentation is hosted via GitHub pages. They are part of the repository and are located in the docs folder. If you change the documentation please regenerate the static site using make docs and include those changes in the PR too. You may find it useful to preview the compiled docs. Run make docs-live to view them in your browser.
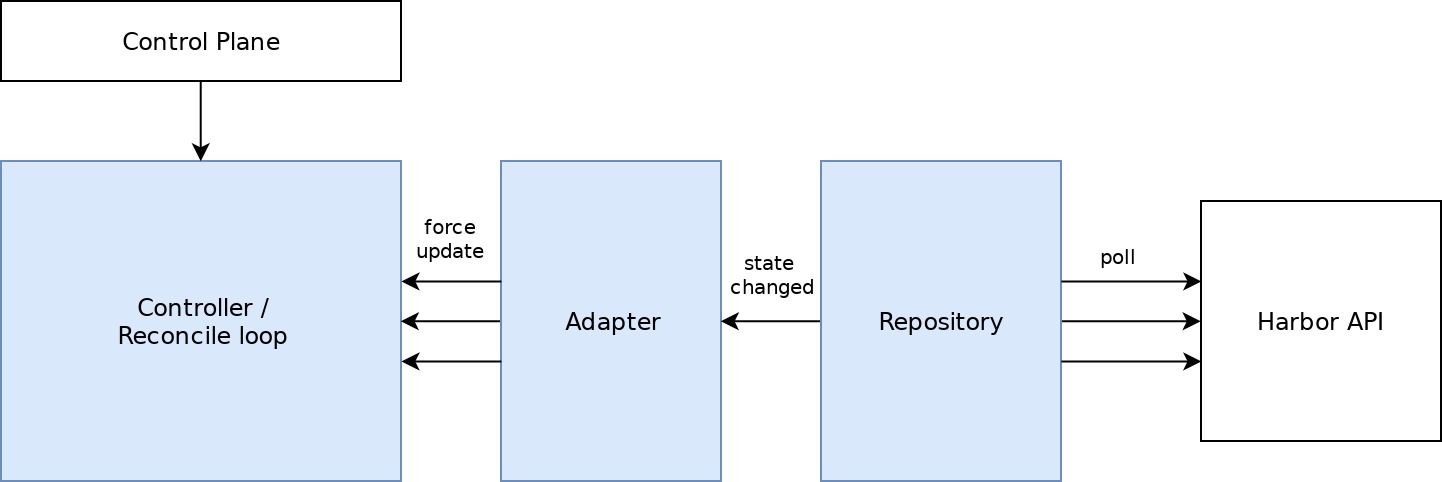
Reconciliation loop
This is pretty straight-forward:
- find harbor projects that match the configured regular expression
- reconcile robot accounts: i.e. (re-)create them if they do not exist, are disabled, expired or we do not manage the token
- find namespaces using a
mappingconfig- for each namespace: create a secret with type
dockerconfigjsonwith the specified name.
- for each namespace: create a secret with type
The reconciliation loop is triggered from essentially three sources:
* Control Plane: whenever a SyncConfig is created/updated/deleted
* Harbor Polling: whenever the state in harbor changes (project or robota account is created, updated, deleted)
* time-based using the configured force-sync-interval: forces reconciliation in a fixed interval to cover cases like namespace creation or robot account expiration
Architecture